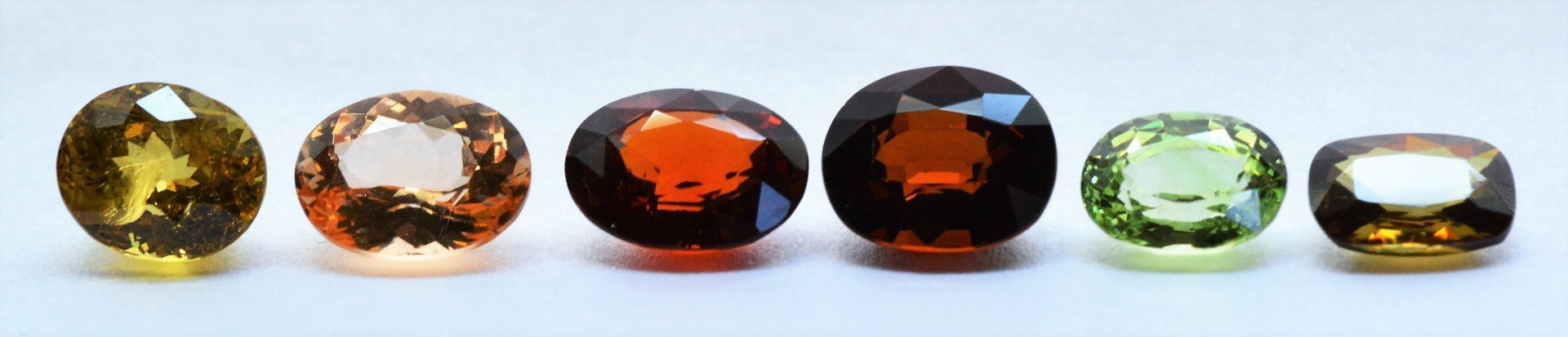
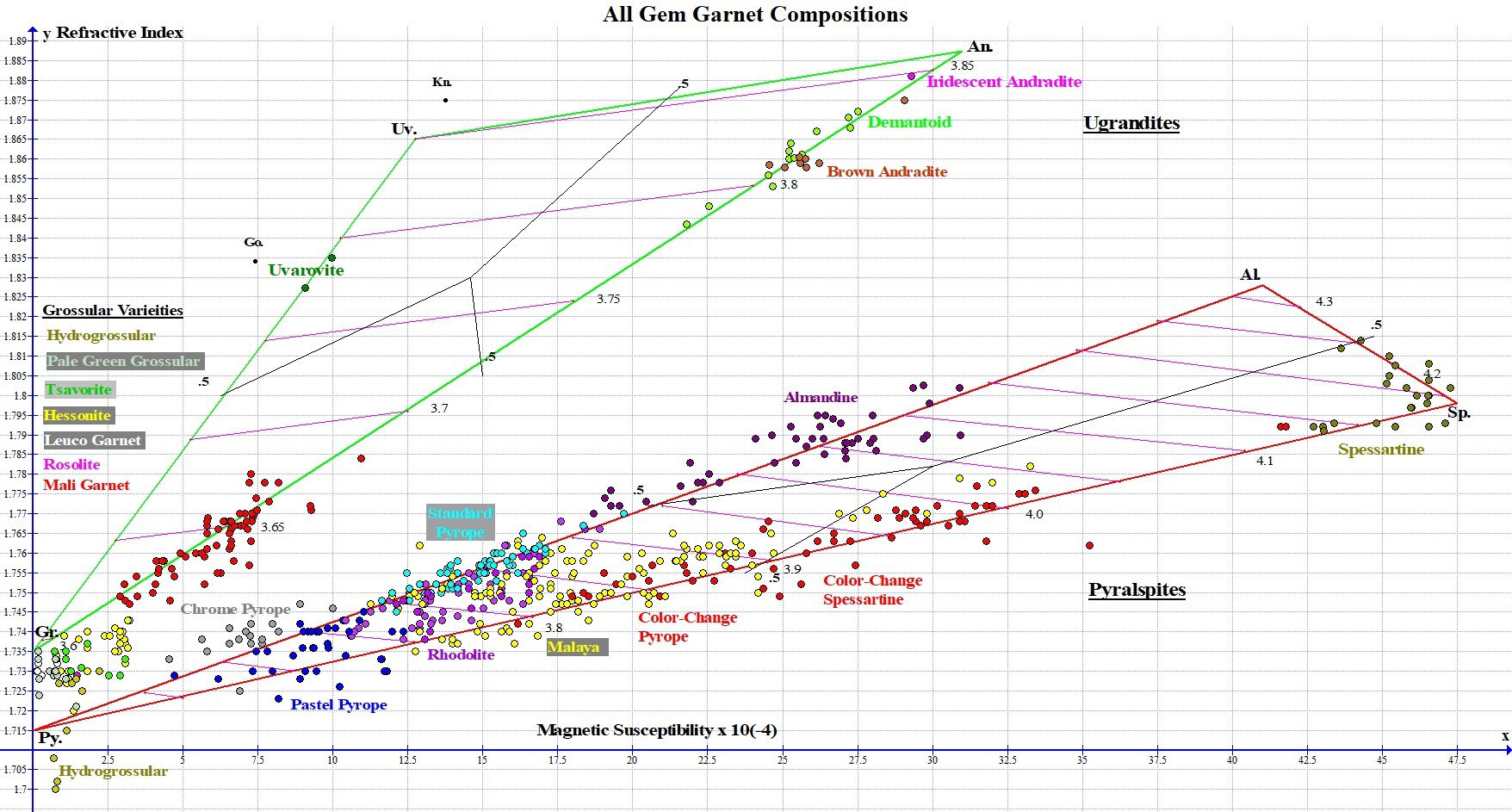
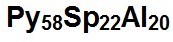A broad sampling of Garnet color is represented on this graph, as well as many rare and unusual Garnets. Species and variety names are color-coded to match the color of their graph points. For the sake of clarity, the numerous Grossular color variety names are listed on the left side of the graph rather than at the site of their graph points. Due to overlapping graph points, not all 500 points on the graph are clearly visible. You can view a larger image of this graph, including gemstone photos, by clicking here.
Graph of All Gem Garnets (over 500 Samples)
Color Change Pyrope
Color Change Spessartine
When we do the calculation for the Malaya Garnet graph point shown above, we find that this particular gem is 58% Pyrope, 22% Spessartine and 20% Almandine. Readers can do this simple calculation after measuring the above lines on a computer screen with a ruler. Mathematics software can also be set up to perform such calculations automatically.
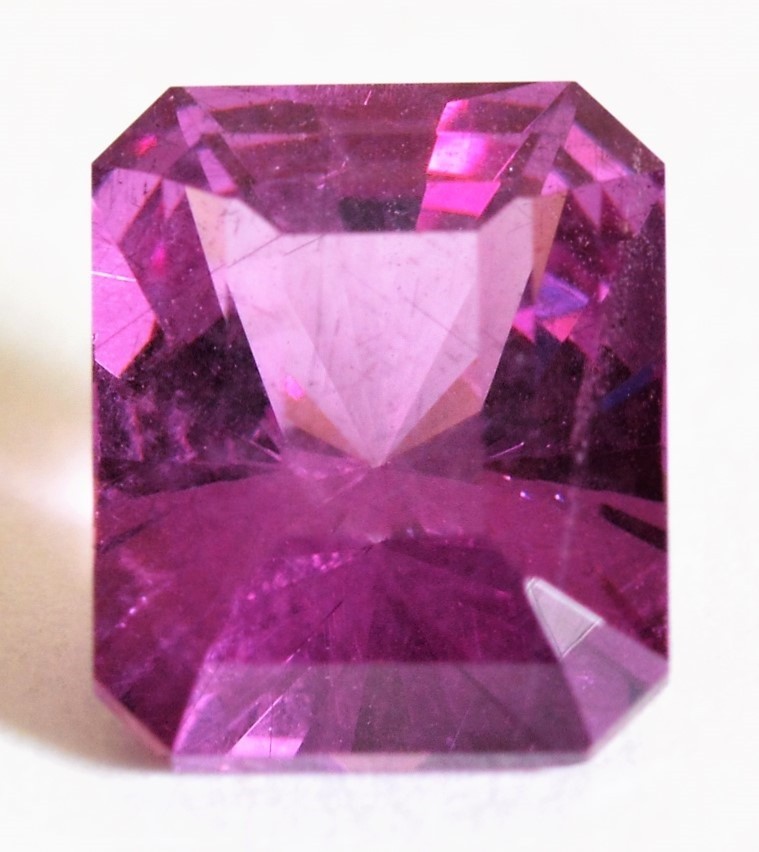
A photograph of the Malaya Garnet represented by the above graph point is shown below, along with a representation of its major composition. Percentages of possible other minor components such as Grossular have not been calculated and are not shown in this representation.
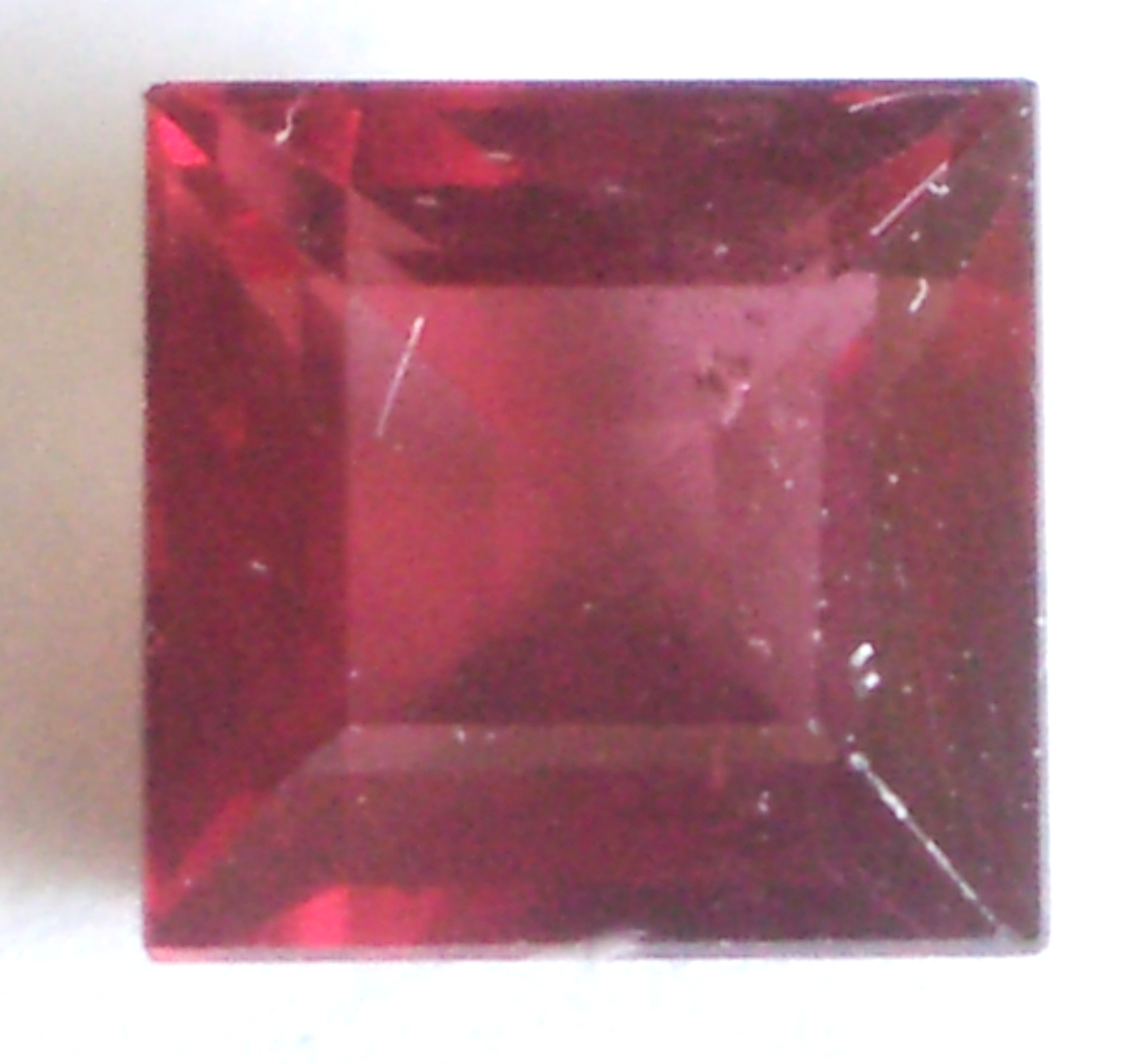
Malaya Garnet
Percentages of the 3 major components of a Malaya Garnet
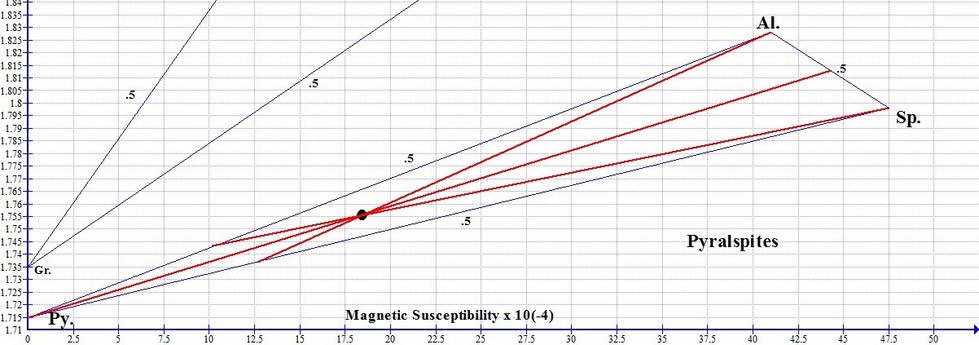
Three Lines Intersect the Malaya Garnet Graph Point
Without any calculations, the approximate composition of this Malaya Garnet is instantly apparent simply by looking at the position of its graph point in relation to the 3 end member species of the ternary. Positioned toward the Pyrope end member, and equidistant from both the Pyrope-Almandine and Pyrope-Spessartine joining lines, we know this gem is predominantly Pyrope with smaller amounts of Almandine and Spessartine in roughly equal amounts. The magnetic susceptibility of this Malaya Garnet is therefor derived equally from the presence of 2 metal ions: iron (Fe2+) and manganese (Mn2+).
Malaya Garnet Graph Point
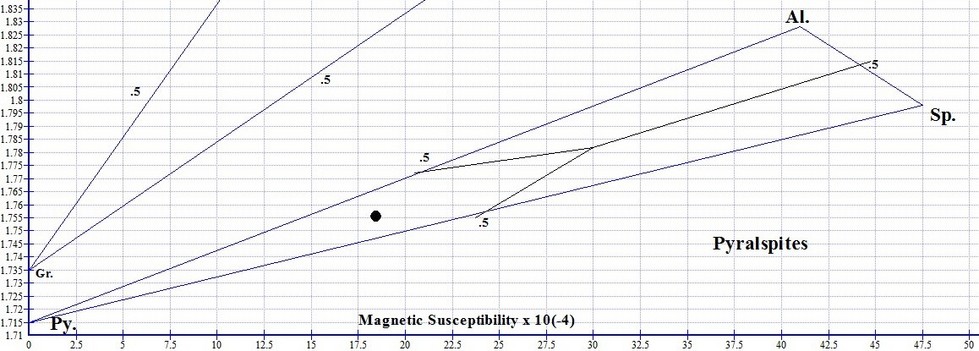
Percentage of composition for each end member species is calculated by measuring the full length of a joining line, then the length of the segment furthest from the apex (between the graph point and where the line ends at the ternary boundary), and finally dividing the far segment length by the full line length. We do this 3 times, once for each line initiating from its end member apex. The 3 percentages of end members should add up to 100%.
Malaya
© Kirk Feral 2011, All Rights Reserved. These materials may be duplicated for educational purposes only. No part of this website may be duplicated or distributed for profit, for commercial purposes, or for posting to another website without the expressed written consent of the copyright holder.
Some Garnet species shown on the All Gem Garnet Graph above have refractive index ranges that do not match exactly the ranges published by GIA. For example, the high RI for Standard Pyrope found in this study is 1.77, while the GIA high is limited to 1.756. In this case, GIA classifies Pyropes with RI's higher than 1.756 as belonging to the hybrid Pyrope-Spessartine species.
The graph above clearly shows that Pyralspite Garnet species mix with each other much more freely than do Ugrandite Garnet species. Ugrandites are composed primarily of one end member or another, with not much in the way of intermediate examples. With the exception of Uvarovite, all Ugrandites tested are in solid solution between Grossular and Andradite, with graph points falling along the Grossular-Andradite joining line. We have not found any Grossular-Andradites that have true intermediate composition, meaning no graph points fall further than a third of the away from the closest end member along the Grossular-Andradite join. Gemologists often refer to Mali Garnet as a Grossuar-Andradite variety, but Mali is better characterized simply as a Grossular Garnet that has higher Andradite content than other Grossular varieties.
Malaya is a Variety of Pyrope
Interpreting the Graph: Based on the location of graph points in this study, we consider Standard Pyrope, Rhodolite, Chrome Pyrope, Pastel Pyrope and Malaya to be varieties of the Pyrope species. Color Change Garnet can be classified as either a variety of Pyrope or Spessartine species, depending on a particular gem's primary composition. This researcher does not consider Color Change Garnet to be a sub-variety of Malaya, as has been suggested by some gemologists. Study results show that Malaya is a variety of Pyrope in the vast majority of cases, but we do find a small percentage of Malayas that are primarily Spessartine. There is considerable overlap in composition among different Pyralspite varieties, particularly between Rhodolite, Malaya and Standard Pyrope. Distinguishing between these can at times be subjective (see page 13).
Determining Percentages of 3 End Member Species
The method described here for determining the proportions of Garnet end-members species within a single Garnet gem was developed by D.B. Hoover in 2008. Results have been shown to be very accurate when gems are primarily composed of 3 end members, as are most Garnet gems other than Pyrope. When additional end-member components are present within a gem, as we find in some Pyrope Garnets that contain 5% or more Grossular or Uvarovite, and/or minor amounts of other end members, accuracy of the calculated percentage of the primary end-member can be reduced by 5% or more.
More often than not among Pyralspite Garnets, graph points of gems fall inside the boundaries of a Garnet ternary rather than exactly along the joining lines that connect two end members. This is particularly true of Rhodolite (purple graph points) and Malaya (yellow graph points) shown in the All Gem Garnet Graph above. Positioning toward the center of the ternary indicates that all 3 endmembers of the ternary are major components of the gem. As an example, below is a graph point for a Malaya Garnet located near the center of the Pyrope trisection of the Pyralspite ternary. This indicates that Pyrope, Almandine and Spessartine are all major components of this Malaya Garnet.
Calculating Percentages of End Members: Using the RIMS method, the exact percentages of each end member species can be easily calculated. We simply use a straight edge to draw a straight line that starts at an end member apex, passes through the graph point, and terminates at the opposite boundary. We do this 3 times, one line from each of the 3 end member apexes as illustrated below.
Graph of All Gem Garnets
Various species of the Garnet mineral group intermix with each other so freely that we find an astonishing variety of gem Garnets. A visual representation or map of how all the gem Garnet species and varieties are related based on known chemical composition is a helpful aid in understanding Garnets. Up until now, no accurate representation of all gem Garnets within a single graph has been available.
Suite of Ugrandite Garnets
Four or More End Members
Although every Garnet, whether a Pyralspite or a Ugrandite, is primarily a mixture of two or three end members from its own series, mixing between two series can also occur, resulting in fourth, fifth and sixth components in minor amounts.
For example, Pyrope Garnets of any variety contain primarily the Pyrope end member along with some Almandine and possibly Spessartine, but they can also contain Grossular, Andradite and Uvarovite. The Grossular content in Pyrope gems is mostly under 5%, but up to 20% Grossular within non-gem (non-transparent) Pyrope has been reported by researchers.
Below is a hypothetical example of the composition of a transparent Standard Pyrope gem, showing percentages of 4 end members, with Grossular as the 4th end member at 5%. The notation shows this hypothetical gem is also composed of 60% Pyrope, 25% Almandine,10% Spessartine and 5% Grossular.
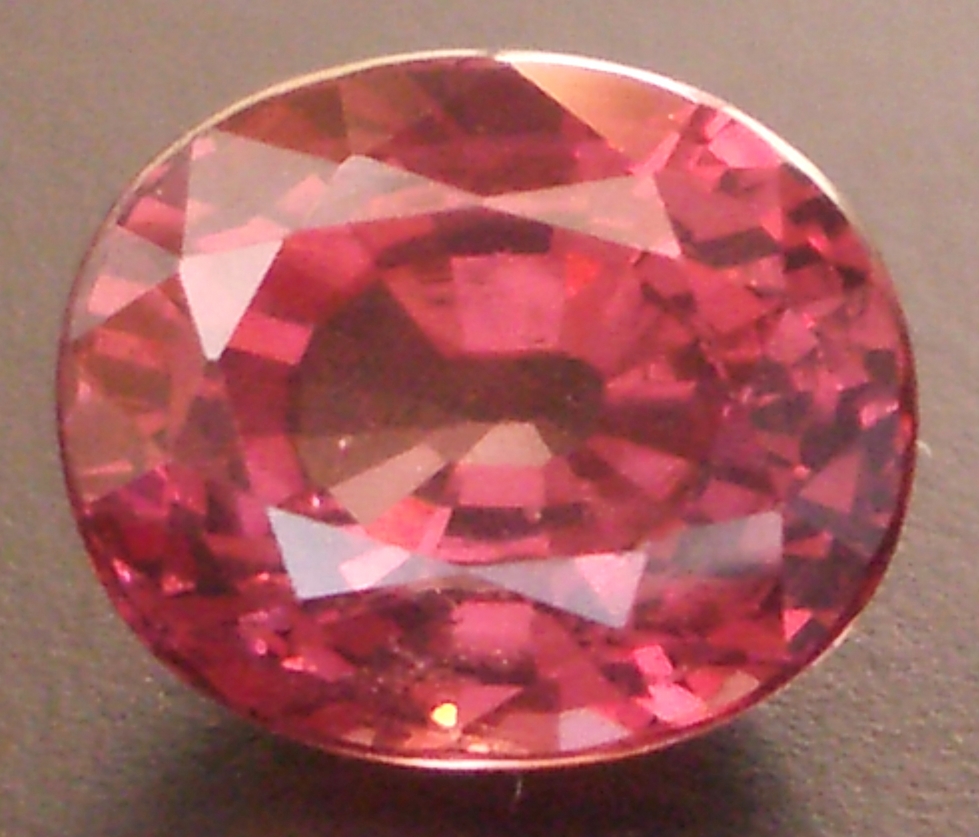
Chrome Pyrope gems such as the one pictured below can contain 4% to 8% chromium from Uvarovite/Knorringite. Any variety of Pyrope Garnet (Standard Pyrope, Chrome Pyrope, Malaya, Rhodolite, Color Change and Pastel Pyrope) can contain some Grossular, where calcium substitutes for magnesium in the A site of the chemical formula for Pyrope. Similarly, Almandine Garnet commonly mixes to a small degree (under 5%) with Andradite Garnet, which is in the Ugrandite series above it. Therefore, Almandine graph points are sometimes positioned above the Pyrope-Almandine boundary line (as seen in the All Gem Garnet graph near the top of this page).
To complicate matters, graph points such as those for most Chrome Pyrope Garnets that are positioned outside a ternary have outside composition, but graph points that lie inside the boundaries of a ternary can also have outside composition. Also, any Garnet graph point that falls on or within the Pyralspite ternary might also fall on a Pyrope-Grossular-Spessartine ternary or a Grossular-Almandine-Spessartine ternary. It's an educated guess as to which end members and how many end members might be present in minor amounts in a particular Garnet gem.
Chrome Pyrope, 1.86ct.
Electron microprobe analysis of the chemical composition of a gem sample from the same parcel as the gem above was conducted in 2014 by Dr. George Rossman at Caltech (California Institute of Technology). Rossman's results showed 1% higher Almandine and 1% higher Spessartine content than our own calculated percentages. Further calculations using the microprobe data showed an additional 5% Grossular content, plus a total of 4% miscellaneous other content that our 3-end member RIMS calculations were unable to discern.
The sum of those additional chemical components reduces our calculated percentage of the Pyrope component from 79% Pyrope to 68%. The Caltech electron microprobe actual percentages were: 68% Pyrope, 12% Almandine, 11% Spessartine, 5% Grossular, 1% Uvarovite/Goldmanite, and 3% un-assigned or unknown remainder.
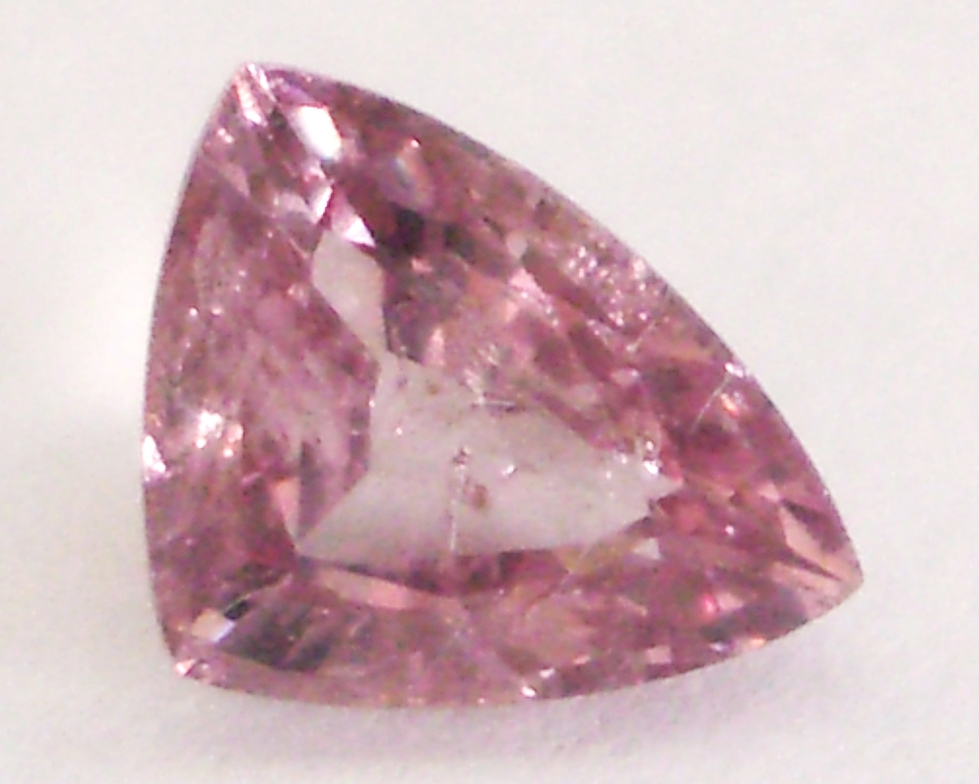
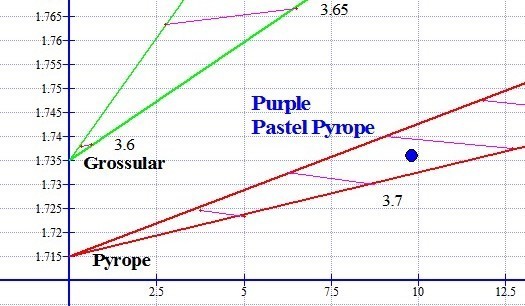
Purple Pastel Pyrope
Calculating accurate percentages of fourth and fifth end members using the RIMS method would require additional y-axis variables such as specific gravity or unit cell length. Percentage calculations for four or more end members would also involve solving simultaneous equations. Such calculations are well beyond the scope and purpose of this website. We also suspect a 3-dimensional representation of the graph would be needed to show the most complete picture of Garnet hybridization and the relationships between Garnet graph points.
Fortunately, a good understanding of Garnet composition does not require any calculations or knowledge of possible fourth or fifth end members. Just looking at the positions of graph points on the All Gem Garnet Graph gives us an accurate snapshot of how different species and varieties intermix within a solid solution series. The RIMS graph for any individual Garnet gem allows us to visually see which two or three Garnet species are the major components of the gem, and provides a visual approximation of the percentage of each major species.
Graph Point
Purple Pastel Pyrope Py79% Al11% Sp10%
A Case Study: The presence of fourth and fifth end members components in significant percentages within a Garnet gem will diminish to some degree the accuracy of 3-end-member calculations when the RIMS Graph method is used. As an example, using refractive index and magnetic susceptibility to calculate the composition of the purple Pastel Pyrope from Tanzania shown below, we determined that the gem composition is 79% Pyrope, 11% Almandine and 10% Spessartine.
Microprobe Calculated Composition
RIMS Graph Calculated Composition
Alternate Ternaries: Because there is some blending between Pyralspites and Ugrandites, additional ternaries can be drawn to reflect this. To calculate Uvarovite content in Chrome Pyrope, we could draw a Pyrope-Uvarovite-Almandine ternary to estimate the chromium (Uvarovite) content in Chrome Pyrope. The 3 end-member calculation would include percentages for Pyrope, Almandine and Uvarovite, while the 4th end-member Spessartine would show as 0%. Similarly, a Pyrope-Andradite-Almandine ternary can be drawn to calculate Andradite content in Almandine Garnets.
Our Graph of All Gem Garnet Compositions pictured below shows results for over 500 Garnet gems tested by this researcher as part of an ongoing study conducted since 2010. This unique graph is the first and only diagram ever published that maps the chemical composition of all known gem Garnet varieties as determined by magnetic susceptibility and refractive index.
Magnetism in Gemstones
An Effective Tool and Method for Gem Identification
© Kirk Feral